Osteopathy and Asthma: Breathing Easy with a Holistic Approach

Asthma affects millions of people worldwide, making it challenging to maintain a good quality of life. While medications such as inhalers remain essential in asthma management, complementary therapies like osteopathy are increasingly recognised for their potential to support respiratory health. By focusing on the relationship between the body’s structure and function, osteopathy offers a hands-on approach to enhance breathing. This article explores how osteopathy can help with asthma, integrating evidence from medical guidelines and academic studies.
What is Osteopathy?
Osteopathy is a holistic healthcare practice that emphasises the interconnection between the body’s structure—muscles, joints, and spine—and its overall function. By addressing imbalances and improving mobility, osteopathy aims to enhance overall well-being. For individuals with asthma, osteopathic techniques target specific areas of the body to improve respiratory efficiency and alleviate symptoms.
How Osteopathy Helps with Asthma
Asthma impacts the body’s mechanics in various ways, from restricting the rib cage’s movement to creating tension in the muscles used for breathing. Osteopathy offers techniques to address these issues, and evidence from academic research and medical guidelines further supports its effectiveness:
Relaxing Respiratory Muscles
The physical strain of asthma can lead to tightness in the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, making breathing more difficult. Osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), such as myofascial release, works to alleviate this tension, promoting smoother respiratory mechanics. The Journal of Osteopathic Medicine highlights that such modular approaches in OMT can enhance breathing efficiency (Schend et al., 2020). Additionally, a Cochrane review suggests that breathing exercises, often incorporated into osteopathic practices, can be beneficial for asthma management (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2013).Enhancing Rib Cage Mobility
Restricted rib cage movement can compromise lung expansion, further aggravating asthma symptoms. Osteopathic techniques focusing on the thoracic spine and rib cage aim to restore flexibility and support better lung function. A case study by the European School of Osteopathy noted that patients who underwent osteopathic interventions experienced improved asthma control and quality of life (European School of Osteopathy, 2018).
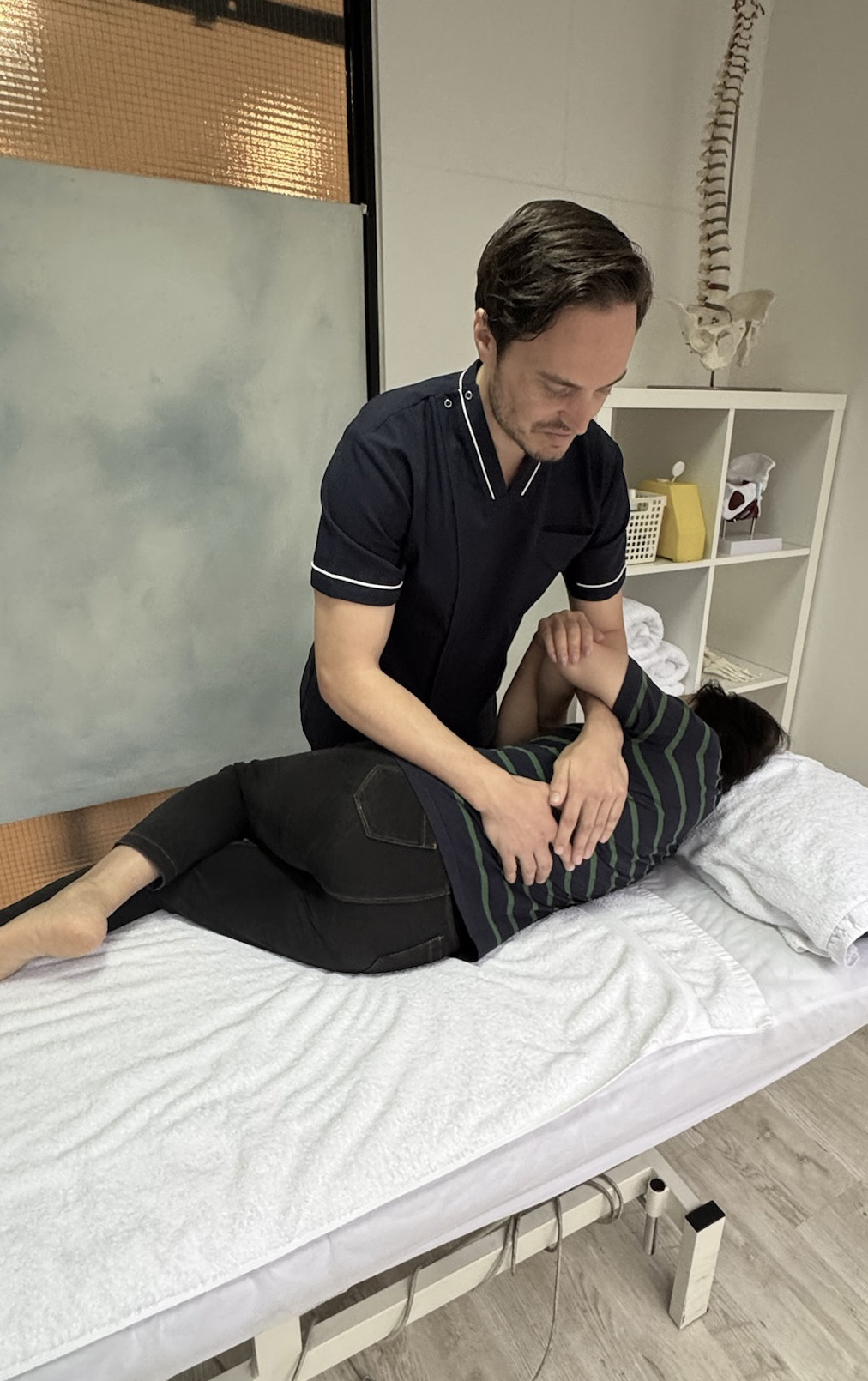
Improving Lymphatic Drainage
Asthma-related inflammation and congestion can lead to airway blockages. Osteopathic techniques like lymphatic pump methods are believed to improve lymphatic circulation, potentially helping to clear excess fluids and toxins from the respiratory system. Research published in the American Academy of Osteopathy Journal supports the role of such techniques in promoting overall respiratory health (Steele, 2019).Optimising Diaphragm Function
As the primary muscle for breathing, the diaphragm plays a central role in maintaining respiratory health. When its function is impaired, asthma symptoms can worsen. Osteopathic methods are used to reduce tension and improve the mechanical movement of the diaphragm. This approach is emphasised in both Foundations for Osteopathic Medicine (Ward, 2015) and medical guidelines, such as those from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), which discuss the importance of optimal respiratory function (NICE, 2021).

Broader Medical Context
Osteopathy is part of a growing trend toward holistic and patient-centred care in asthma management. Globally respected guidelines, such as those from the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), highlight the importance of non-pharmacological strategies in complementing traditional asthma treatments (GINA, 2022). Similarly, the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) recognise the role of holistic care, including physical therapies, in supporting asthma patients (BTS and SIGN, 2019). These guidelines provide a strong foundation for understanding how osteopathy can fit within broader asthma care plans.
Why Consider Osteopathy for Asthma?
Asthma management often focuses on medications and avoiding triggers, but osteopathy offers a complementary path. By addressing the structural and functional factors that influence breathing, osteopathy can help patients feel more in control of their symptoms. It is, however, essential to remember that osteopathy is not a substitute for traditional asthma treatments. Consulting a qualified osteopath and discussing your options with your healthcare provider ensures that your care plan is safe and effective.
References
British Thoracic Society (BTS) and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN), 2019. British guideline on the management of asthma. [online] Available at: <https://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk > [Accessed 27 March 2025].
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2013. Breathing exercises for asthma. [online] Available at: <https://www.cochranelibrary.com> [Accessed 27 March 2025].
European School of Osteopathy, 2018. Cranial osteopathy and asthma: a case study. Maidstone: European School of Osteopathy.
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), 2022. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. [online] Available at: <https://www.ginasthma.org > [Accessed 27 March 2025].
Jackson, K.M. and Steele, K.M., 2005. Osteopathic treatment of asthma: A literature review and call for research. West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine.
Journal of Osteopathic Medicine, 2020. ‘Osteopathic modular approaches to asthma’, Journal of Osteopathic Medicine, 120(4), pp. 45–53.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), 2021. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management. [online] Available at: <https://www.nice.org.uk > [Accessed 27 March 2025].
Osteopathy Australia, 2023. Holistic and patient-centred osteopathic care: position statement. [online] Available at: <https://www.osteopathy.org.au > [Accessed 27 March 2025].
Schend, J., Rowane, M., Sanan, N. and Hostoffer, S.R., 2020. An osteopathic modular approach to asthma: A narrative review. Journal of Osteopathic Medicine, 120(4), pp. 45–53.
Steele, K.M., 2019. ‘Lymphatic pump techniques and asthma: a review’, American Academy of Osteopathy Journal, 30(6), pp. 12–20.
Ward, R.C., 2015. Foundations for osteopathic medicine. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.


